What is the ITR 4?
ITR-4 Form is that the tax Return form for the taxpayers who choose a presumptive income scheme under Section 44AD, Section 44ADA and Section 44AE of the tax Act.
However, if the turnover of the business mentioned above exceeds Rs 2 crores, the taxpayer will need to file ITR-3.
Overview
Who is required to file ITR 4?
ITR 4 is to be filed by the individuals/HUF/ Partnership firm whose total income of AY 2020-21 includes as below:
-
Business income under section 44AD or 44AE
-
Income from profession calculated under section 44ADA
-
Salary/pension having income up to Rs 50 lakh
-
Income from One House Property having income up to Rs 50 lakh (excluding the brought forward loss or loss to be carried forward cases under this head)
-
Income from Other Sources having income up to Rs 50 lakh (Excluding winning from lottery and income from horse races).
Note: Freelancers engaged within the above profession also can choose this scheme if their gross receipts don’t exceed Rs 50 lakhs.
Who isn't required to file ITR 4 for AY 2021-22?
-
An individual having income from salary, house property or other sources above Rs 50 lakh cannot use this type .
-
An individual who is either a director during a company and has invested in unlisted equity shares cannot use this type .
-
An individual, HUF or partnership firm whose books of accounts should be audited under the tax Act, 1961.
What is the Structure of ITR 4?
ITR-4 is split into parts as mentioned below:
PART A: General Information

PART B: Gross total income from the five heads of income

PART C: Deduction and total taxable income

PART D: Tax computation and tax status

Schedule BP: Details of income from Business-Section 44AD, 44ADA and 44EA

Information regarding turnover/Gross receipts reported for GST
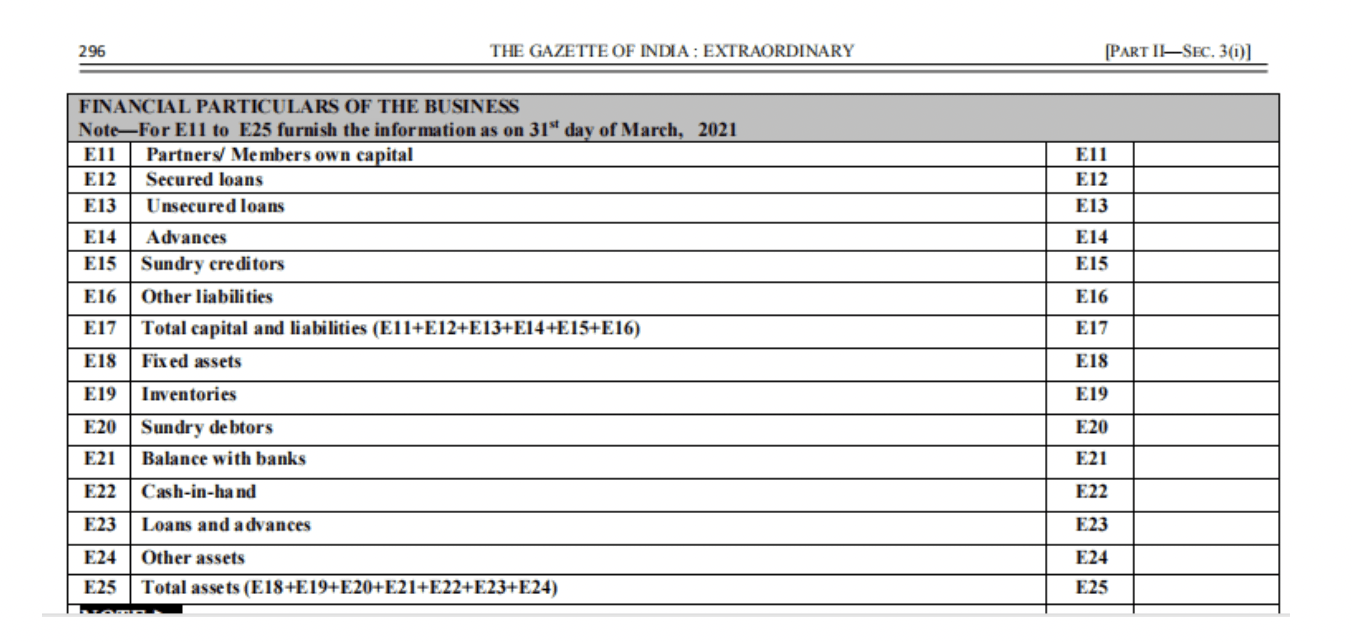
Financial Particulars of Business
Schedule IT, TCS and TDS 1: Statement of payment of advance tax and tax on self-assessment, tax collected at source and TDS from salary
Schedule IT, TCS and TDS 1: Statement of payment of advance tax and tax on self-assessment, tax collected at source and TDS from salary

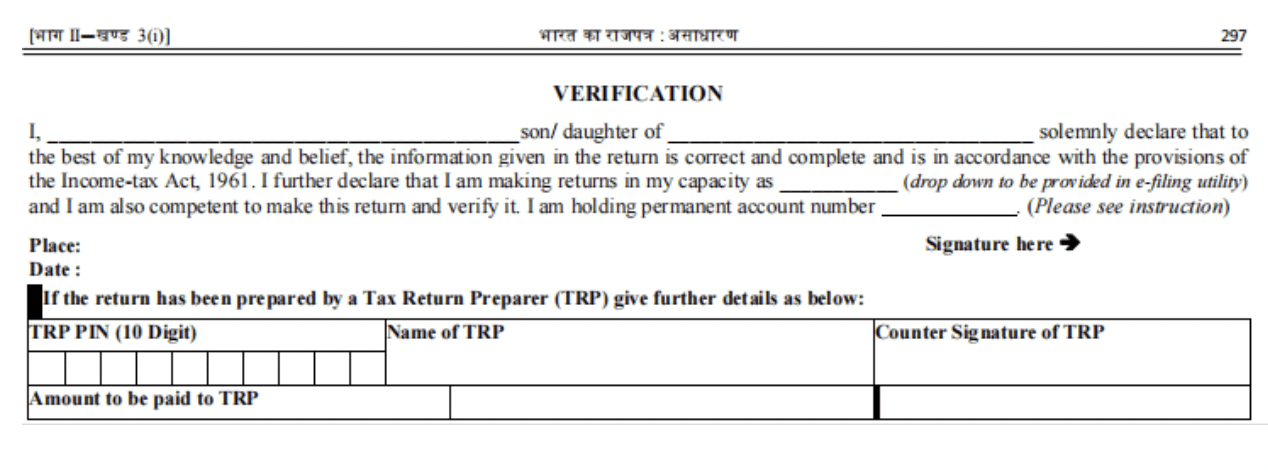
Verification column

What is Limited Liability partnership (LLP) Registration ?
LLP is an alternative corporate business form that gives the benefits of limited liability of a company and the flexibility of a partnership. • The LLP can continue its existence irrespective of changes in partners.
How do I file my ITR-4 Form?
You can submit your ITR-4 Form either online or offline.
Offline
The ITR form are often filed offline only in any of the subsequent case:
-
Individual is of the age of 80 years or more.
-
The income of the individual is a smaller amount than Rs 5 lakhs and who don’t need to claim a refund within the tax return
The return are often filed offline within the following ways :
-
By furnishing a return during a physical paper form
-
By furnishing a bar-coded return
The tax Department will issue you an acknowledgement at the time of submission of your physical paper return.
Online/Electronically
By furnishing the return electronically under digital signature –
-
If you submit your ITR-4 Form electronically under digital signature, the acknowledgement are going to be sent to your registered email id. you’ll also prefer to download it manually from the tax website.
-
By transmitting the info electronically then submitting the verification of the return reciprocally Form ITR-V- you’re then required to sign it and send it to the tax Department’s CPC office in Bangalore within 120 days of e-filing.
Remember that ITR-4 is an annexure-less form i.e. you are doing not need to attach any documents once you send it.
Major Changes made in ITR-4 for AY 2021-22
-
There are not any major changes in ITR 4 as compared to last year.
-
ITR 4 for AY 2021-22 are updated with a declaralation for selecting between old and new tax regimes. The declaralation is under Part A- general information as ‘ Are you choosing new tax regime under section 115BAC (Yes or No). If yes , please furnish the date of filing of Form 10IE alongwith acknowledgement number’.
-
Part B- Under income from other sources, a drop-down like interest from saving account, deposit etc to be provided within the e-filing utility specifying nature of income. within the case of dividend income, quarterly breakup to be provided for allowing applicable relief from the charge of interest for default in payment of advance tax under section 234C.
-
Schedule DI that was inserted for AY 2020-21 has been removed.
Major Changes made in ITR-4 for AY 2020-21
-
Individual taxpayers who meet the standards of (a) making cash deposits above Rs 1 crore with a bank or (b) incurring expense above Rs 2 lakh on foreign travel or (c) expenditure above Rs 1 lakh on electricity should also file ITR-1. The taxpayer should indicate the quantity of the deposit or expenditure.
-
Under Part A, ‘Govt’ checkbox stands changed to ‘Central Govt’ and ‘State Govt’, and a checkbox ‘Not applicable (e.g. family pension etc.) has been introduced under the ‘Nature of employment’ section.
-
Return filed under section has been segregated between normal filing and filed in response to notices.
-
The ‘Schedule VI-A’ for tax deductions is amended to incorporate deduction under section 80EEA and section 80EEB. A sink is provided to enter details of donations under section 80G
-
In ‘Schedule BP’, gross turnover or gross receipts to incorporate revenues from prescribed electronic modes received before the required date.
-
the small print of tax write-off claims for investments or payments or expenditure made between 1 April 2020 until 30 June 2020.
Major Changes made in ITR-4 for AY 2019-20
-
ITR 4 form for FY 2018-19 isn’t applicable to a private who is either a director of a corporation or has invested in unlisted equity shares.
-
Under Part A, ‘Pensioners’ checkbox has been introduced under the ‘Nature of employment’ section.
-
Return filed under section has been segregated between normal filing and filed in response to notices.
-
Deductions under salary are going to be bifurcated into standard deduction, entertainment allowance and professional tax.
-
80G Deduction: Amount of Donation is bifurcated into cash and other mode.
-
Separate Business details like Name of business, business code, description for section 44AD, 44ADA & 44AE.
-
New fields under section 44AE has been introduced like Registration No. of products carriage, Whether owned/leased/hired, Tonnage Capacity of products carriage (in MT), No. of months that goods carriage was owned/leased/hired by assessee etc.
-
Under GST details the turnover text has been replaced by “Annual value of outward supplies as per the GST returns filed”.
-
‘Deemed to be let loose property’ option now available under ‘Income from house property’.
-
The taxpayers are going to be required to supply income wise detailed information under the ‘Income from other sources’.
-
A separate column is introduced under ‘Income from other sources’ for deduction u/s 57(iia) – just in case of family pension income.
-
Section 80TTB column has been included for senior citizens.
Presumptive Income & its Taxation – under section 44AD
When you are running alittle business, you’ll not have enough resources to take care of proper accounting information and calculate your profit or loss. This makes it difficult to stay track of your income and taxes from such a business.
With this in mind, the tax Department has laid out some simple provisions, where your income is assumed supported the gross receipts of your business. This method is named the presumptive method, where tax is paid on an estimated basis.
Features of this Scheme
Your net is estimated to be 8% of the gross receipts of your business. But from FY 2016-17, if gross receipts are received through a digital mode of payment, then net is estimated at 6% of such gross receipts and for cash receipts. However, the speed is that the same at 8% of such cash receipts.
-
You don’t need to maintain books of accounts of this business.
-
You need to pay 100% Advance Tax by 15th March for such a business.
-
No got to suits the need of quarterly instalments due dates (June, sep, Dec) of advance tax.
In case of Advance Tax, the advantage of paying the advance tax in one instalment by 15th March is merely granted for the business that this scheme has been opted for. If the taxpayer has income which is aside from from such business, where his liabilities exceeds Rs 10,000 during a year, he has got to pay advance tax on such other income
-
You aren’t allowed to deduct any business expenses against the income.
If you’re running quite 1 business, the scheme has got to be chosen for every business. for instance , if you run 3 businesses where just one is assessed under section 44AD. The relief of not maintaining accounting records & no audit requirement is merely applicable to the business to which this scheme applies. For other 2 businesses which aren’t covered under this section – the accounting records need to be maintained and audit is additionally required.
Eligibility Criteria for this Scheme
-
Your gross receipts or turnover of the business that you would like to avail this scheme should be but Rs 2 crore.
-
You must be a ‘Resident’ in India. The scheme isn’t applicable to non-residents.
-
This scheme is allowed to a private , a HUF or a partnership firm. it’s not available to a corporation or an LLP (Limited liability partnership).
-
The scheme can’t be adopted by the taxpayer, if he has claimed deduction under section 10, 10A, 10B, Section 10BA, or Section 80HH to 80RRB within the relevant year.
Not sure which ITR form you would like to use? Read our guide for help.
Eligible Businesses
-
The taxpayer could also be in any business – retail trading or wholesale trading or civil construction or the other business to avail this scheme.
-
But this method of income computation isn’t applicable to:
-
Income from commission or brokerage
-
Agency business
-
Business of plying, hiring or leasing goods carriage (see section 44AE)
-
Professionals – who are carrying on a profession of legal, medical, engineering, architectural, accountancy, technical consultancy, interior decoration, a licensed representative, film artist, company secretary and knowledge technology. Authorized representative means – a person , who represents someone, for a fee or remuneration, before any Tribunal or authority under any law. Film Artist includes a producer, actor, cameraman, director, conductor , stage director , dance director, editor, singer, lyricist, story writer, screenplay writer, dialogue writer, dress designer – basically a person who is involved in his professional capacity within the production of a movie .(see Sec 44ADA). These are the professions listed under section 44AA(1).
Let us consider an example:
Devesh runs a medical shop in his colony. The receipts of his business are Rs 1,50,00,000 within the fiscal year 2020-21. Can Devesh take advantage of the scheme under section 44AD?
Devesh may be a resident and his receipts from this business are but Rs 2 crore. His business isn’t listed under the non-eligible businesses list and thus he can avail the advantage of this scheme under section 44AD.
Deduction for Business Expenses
No business expenses are allowed to be deducted from internet income. Depreciation is additionally not deductible.
However, within the case of a partnership firm, a separate deduction for remuneration of partners and interest paid to partners is allowed. This must be within the limit specified under section 40(b).
Even though depreciation isn’t allowed as a deduction, written down value (WDV) of the assets shall be considered as if depreciation has been allowed.
For example, Rohit runs a Kirana shop and his gross receipts are Rs 75,12,260 from this business. He decided to choose the scheme under section 44AD. He also wants to say depreciation for 1 large refrigerator and a computer with a billing system he purchased for Rs 2,50,500. He also spent Rs 1,50,000 buying new racks for displaying his goods.
Since Rohit has opted for the presumptive scheme under section 44AD, his net is computed as 8%(assuming all cash receipts) of Rs 75,12,260 = Rs 6,00,981. Under this scheme, no deductions are allowed from income. Rohit won’t be allowed to deduct depreciation from this income. He cannot deduct expenses for the acquisition of the new rack.
Can the taxpayer declare higher or lower income than 8% of gross receipts?
The taxpayer can voluntarily declare a better income and pay tax thereon . just in case the taxpayer chooses to declare lower income than 8% of gross receipts – he shall need to maintain books of accounts and obtain them audited.
For example, Ritesh runs a stationery shop and his turnover from this business are Rs 85,20,000. He wants to choose the scheme under section 44AD and thus his income shall be Rs 6,81,600 (at 8% of gross receipts, assuming all cash receipts).
However, Ritesh’s actual income from the business works bent Rs 5,74,000. Ritesh decides to not choose the scheme under section 44AD and pay tax on the particular income of his business. However, since he’s not choosing this scheme he has got to maintain proper accounting records and also get his records audited.
Computing Turnover or Gross Receipts :
Gross receipts or Turnover mean the entire collections of the business. The receipts shall be inclusive of GST. The receipts shall also include delivery charges also as receipts from the sale of scrap.
Discounts given, advances received and money received on sale of assets should be excluded.
Presumptive taxation under Section 44AE
For those that are within the business of plying, leasing or hiring of trucks a scheme almost like presumptive income scheme under section 44AD is out there .
Eligibility Criteria:
-
You should be within the business of plying, leasing or hiring goods carriages.
-
You shouldn’t own quite 10 goods carriages at any time during the year. Include carriages taken on hire purchase or on instalments.
-
You could also be a private , HUF, Company or partnership firm
Features of this scheme:
-
Net taxable income from a goods vehicle (including any goods carriage) are going to be calculated as Rs 7,500 per month for every vehicle per month or part thereof during the FY during which the vehicle is owned by the assessee.
-
The above calculation are going to be regardless of heavy goods vehicle (more than 12000 kgs) and lightweight goods vehicle(less than or adequate to 12000 kgs).
-
The assessee isn’t required to take care of books of accounts under this business
-
The advance tax has got to be paid 100% by 15th March for such businesses.
Deduction for Business Expenses:
-
No business expenses are allowed to be deducted from internet income. Depreciation is additionally not deductible.
-
However, within the case of a partnership firm, a separate deduction for remuneration of partners and interest paid to partners is allowed. This must be within the limit specified under section 40(b).
-
Even though depreciation isn’t allowed as a deduction is written down value (WDV) of the assets shall be considered as if depreciation has been allowed.
Let’s see the calculation with an example,
Can the taxpayer declare higher or lower income?
-
Rohan is engaged within the business of plying, hiring or leasing goods carriages, and owns 5 trucks and another 2 trucks which are taken on installments. Rohan wants to understand what is going to be his income from this business?
-
Rohan can choose the scheme under section 44AE since he earns but 10 trucks. He owns 7 trucks in total, include trucks which are purchased on installments albeit some installments are unpaid.
-
Rohan’s income from this business shall be Rs 7 trucks x Rs 7,500 x 12 months = Rs 6,30,000 shall be Rohan’s net from this business. No business expenses are often claimed from this income.
Can the taxpayer declare higher or lower income?
The taxpayer can voluntarily declare a better income and pay tax thereon . just in case the taxpayer chooses to declare lower income than as mentioned above – he shall need to maintain books of accounts under section 44AA and obtain them audited.
Presumptive taxation under Section 44ADA
The advantage of Presumptive tax rates was only available to businesses. But now this benefit has been extended to professionals also. it’ll be applicable to the professionals, whose total gross receipts doesn’t exceed Rs 50 lakhs during a fiscal year .
Presumptive Tax Rate:
The income of the professionals choosing this scheme would be assumed at 50% of the entire gross receipts for the year.
Applicability of the scheme:
The scheme is applicable only to a resident assessee, who is a private , HUF or Partnership and not LLP (Limited Liability Partnership Firm). The persons engaged within the following profession can choose this presumptive Income scheme:
-
Medical
-
Engineering
-
Legal
-
Architectural Profession
-
Accountancy Profession
-
Technical Consultancy
-
Interior Decoration
No requirement of Maintenance of books of Account:
Professionals choosing this scheme needn’t maintain books of account required under section 44AA. They also needn’t get the books of account get audited under section 44AB.
Deduction for Business Expenses:
No trade expense is allowed to be deducted from internet income. Depreciation is additionally not deductible. albeit depreciation isn’t allowed as a deduction. Written down value (WDV) of the assets shall be considered as if depreciation has been allowed.
Can the taxpayer declare higher or lower income?
The taxpayer can voluntarily declare a better income and pay tax thereon. just in case the taxpayer chooses to declare lower income than 50 you look after the entire gross receipts- he shall need to maintain books of accounts under 44AA and obtain them audited.